The hunt for talent is more intense than ever. A survey executed by Indeed found that 86% of hiring managers and recruiters believe that it is challenging to find and hire software engineers. So, as you know, it is a competitive scenario for tech companies that need to look for a faster and cheaper solution of hiring talents to scale their product engineering team.
Due to the high demand for IT outsourcing, micro-sourcing has been taken into consideration for some of the organizations in order to reduce the operational cost, increase revenue and decrease employee pressure.
According to the Crowdsourcing Industry Report, demand in the global micro sourcing industry is driven by start-up and small companies. Collectively they account for over 60% of the market revenues. Start-up companies drive the majority of the revenues in the industry, contributing 39% of the total revenues.
But is this model really efficient compared to the other outsourcing methods? Are there hidden costs of using this method on your Software Development Lifecycle? Keep reading this article to find out!
What is Microsourcing?
Gartner defines microsourcing as the process of breaking up large projects into smaller projects. This method involves sourcing tasks from existing providers to enable a more agile approach for a quicker turnaround and better results at competitive pricing.
Some examples of tasks commonly outsourced by micro sourcing are data entry and validation, image tagging, research, writing, editing, categorization, maintenance of databases, data back-up/ recovery, and data protection.
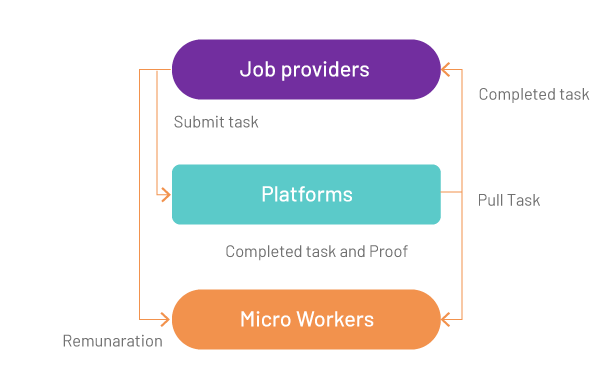
Microsourcing is very common in Asian countries such as Malaysia, where this kind of outsourcing was worth US$1.9 billion in 2013. Fostered especially by the government, the Malaysian micro-sourcing involved three main stakeholders:
- Job Providers: companies that outsource their jobs to micro sourcing platforms.
- Platforms: which mediate the micro-tasks between the job providers and the Micro workers
- Microworkers: who execute the micro-tasks
Interactions go somewhat like this:
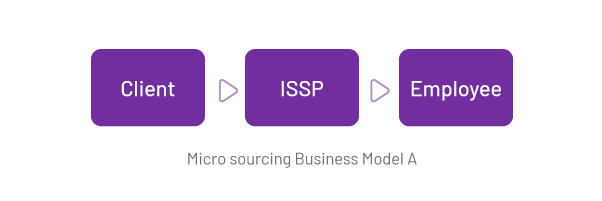
Types of micro sourcing
- Model A: The ISSP (Impact Sourcing Service Providers) owns the outsourcing contract and interacts with the client. The ISSP delivers the service to the client, owns the outsourcing center, and manages local employees to perform the day-to-day outsourced tasks.
 Model B: The ISSP owns the outsourcing contract and interacts with the client. However, the ISSP uses a sub-contractor to deliver the service and perform the day-to-day outsourced tasks. More than one sub-contractor can be used in this model. The ISSP retains overall accountability for the contract and service provision.
Model B: The ISSP owns the outsourcing contract and interacts with the client. However, the ISSP uses a sub-contractor to deliver the service and perform the day-to-day outsourced tasks. More than one sub-contractor can be used in this model. The ISSP retains overall accountability for the contract and service provision.

What are the differences between Microsourcing and Outsourcing?
Microsourcing is different from traditional outsourcing. You don’t hire one or two full-time employees. Instead, you leverage the special skill-set of numerous workers. Each person has one job to do for your business.
| Outsourcing | Microsourcing | |
| Costs | Low | Low |
| Long term costs | High | Varies |
| Process Expertise | High | Medium |
| Operational Flexibility | High | High |
| Operational Control | Low | Medium |
What are the strategic reasons to use microsourcing?
The main reason to use a microsourcing strategy is to save money. Once you pay workers as a service (instead of paying a lump fee), it may seem like a great money-saving strategy.
In addition to that, research from the School of Information Management, Victoria University of Wellington (New Zealand), listed some advantages like the facility to delineate and divide the project into pieces and the possibility to run the project entirely online.
What are the risks of microsourcing?
According to research published by University Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia, there are some gaps in the micro sourcing model. As the roles in the local micro sourcing industry are not as wide as international platforms, when a task is advertised on a platform, micro workers will pull the task based on their interests.
After the task is completed, the micro worker will submit it together with proof of the completed task to the platform. Once the task is verified as completed by the platform, the macro worker will get paid directly by the job provider.
However, the tasks available in the market are not targeted to any specific micro workers and these workers are not given proper training to perform the task. The existing scenario could make the industry unsustainable in the long run because it hinders retaining top tech talent or customizing SDLC team members’ roles.
What is the hidden cost of microsourcing?
The main hidden cost of microsourcing is to support the sustainability of the Micro sourcing Ecosystem, because there is lacking skilled/ experienced talents across the microsourcing workers.
That’s why also there is a need to develop skilled and experienced talents as well as project management and business development teams to support micro sourcing platforms. Therefore, there is a need to incentivize training and skilling of talents to ensure this method’s sustainability.
Engagement with professional organizations, particularly those in the field of micro sourcing and outsourcing advisory services is important to spread awareness and understanding of what micro sourcing can offer. These organizations can provide leadership and promote sharing of solutions and best practices, as well as spur new business process management and innovation.
The micro sourcing industry ecosystem involves foreign interviews with many stakeholders with their own agenda and objectives. As with any established industry, proper monitoring or regulatory bodies are required to supervise fair play, employ equitable standards, and prevent the exploitation of its players, particularly the employees.
The role of the workplace is changing with technology development, combined with an increasingly cross-generational and distributed workforce, challenging traditional concepts of the workplace. Thus, the implementation of the Strategic Framework requires strong governance and leadership, mandated actions where appropriate, enforcement via spending controls, and monitoring and reporting.
In addition, potential job providers from the public sector have concerns about the local micro sourcing mechanism such as data confidentiality and payment mechanisms. These issues need to be addressed to get their confidence in the industry.
Cost of tech talent in Southeast Asia
By 2040, Asia will likely account for almost 40% of global consumption and generate more than 50% of world GDP, says a McKinsey Global Institute Paper.
In addition to that, the rise of Asian startups has pushed larger organizations to accelerate their digital efforts as well, leading to high demand for tech talent across all industries and sectors.

Talent shortage is already a reality in SouthEast Asia, too. Source: https://www.robertwalters.com.sg/content/dam/robert-walters/country/singapore/files/whitepapers/robert-walters-singapore-five-lessons-in-tackling-the-tech-talent-shortage.pdf
A person working as a Software Engineer in Vietnam typically earns around 17,4000,000 VND per month (circa de USD 755,57). Salaries range from 8,370,000 VND, around USD 364,35 (lowest) to 27,400,000 VND, around USD 1.190 (highest).
In Malaysia, salaries can vary from RM 47,415 per year, around USD 11,700 to RM 87,100 per year, around USD 21.500.

Source: https://malaysia.indeed.com/career/software-engineer/salaries
Tech talent in India keeps a very similar average salary. The average application software developer is ₹501,874 around USD 6,888, according to UpGrad Blog. An entry-level application software developer can earn around ₹345,016 per annum (around USD 4,735) with less than one year of experience. Early level application software developers with 1 to 4 years experience get around ₹442,241 per annum around USD 6,069.
A mid-level application software developer with 5 to 9 years of experience earns ₹873,499 around USD 11,988 per annum in India. As your experience and skills grow, your earnings rise dramatically as senior-level application software developers earn ₹1,397,624 a year in India around USD 19,182.
Considering the big difference between time zones from southwest Asia and the US, and also talent quality vs. quantity cost-benefits, it may be more advantageous for these companies to build Nearshore Teams instead of a quick microsourcing hire.
In fact, US organizations already registered an average of 38% to 48% savings in labor costs by outsourcing IT functions to Central and South America. Considering that an engineer can cost on average USD 150k in New York, plus a fringe of about 20% and this US-based engineer will come out at USD 180k (minimally) and Brazilian Engineer equivalent will cost from USD 90 to 110k, you may be wasting time and money on microsourcing.
How to solve the problem of outsourcing in technology teams
In order not to be fooled by a false sense of economy, it is essential that you place all hidden costs on the table. If microsourcing seems very advantageous at first, when we start to investigate better the quality versus the quantity of the work developed, we conclude that all the effort may not be worth it. Therefore, the nearshore is a much more interesting option for those who need to scale technology teams efficiently and quickly.
At Ubiminds, we source, recruit, and hire qualified IT engineers for companies and help them structure distributed teams. Our community of almost 10,000 product designers, security engineers, quality analysts, software developers, and architects is ready to be tapped.
Our success-based pricing model is great for any client’s bottom line. Clients look to us to provide top-notch team members who desire career opportunities, and not project-based short term work. Most engagements are at least one year and in some cases more than 3 years. We work with annual agreements and there are no hidden fees.
If you already know us and would like to know more benefits of Ubiminds, contact your CSM. If you don’t know us yet, take this opportunity and fill the form below!

International Marketing Leader, specialized in tech. Proud to have built marketing and business generation structures for some of the fastest-growing SaaS companies on both sides of the Atlantic (UK, DACH, Iberia, LatAm, and NorthAm). Big fan of motherhood, world music, marketing, and backpacking. A little bit nerdy too!



 Model B:
Model B:


