Building successful distributed teams, similar to remote teams or virtual teams, offers access to a global talent pool and unlocks the potential of a global workforce. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about creating and managing high-performing distributed teams. Get quick tips on preventing communication gaps, making the most of time zone differences, and leveraging cultural disparities to build a thriving distributed workforce that drives success.
[ez-toc]Understanding the dynamics of such teams is crucial for driving productivity, innovation, and success across global operations. This guide will walk you through the essential elements that make distributed teams excel, from communication strategies to leveraging technology and fostering a strong team culture.
From Colocated to Global: Understanding Different Team Models
The global talent shortage is real, with millions of unfilled positions across various industries. Studies point out there is a shortage of at least 1.4 million software developers and only 400,000 software developer graduates in the USA.
And there’s more: it’s projected that this gap will continue to grow for at least the next ten years. Distributed teams allow you to tap into a wider pool of skilled professionals, regardless of location.
Whether you’re a startup seeking specialized skills or a mature company aiming to optimize resources, distributed teams offer numerous advantages. Learn the essential strategies to overcome challenges, foster collaboration, and build a thriving remote workforce, regardless of location or time zone.
Colocated, Remote, Hybrid, and Distributed Teams: Key Differences
Not all remote teams are created equal. To effectively build and manage high-performing teams, it’s crucial to understand the nuances between different work models:
- Colocated Teams: All members work together in a physical office.
- Remote Teams: Employees work from different locations, often within the same country or time zone.
- Hybrid Teams: A combination of colocated and remote work, with employees splitting time between office and remote settings.
- Distributed Teams: Members are geographically dispersed across different countries and time zones.
Each model presents unique opportunities and challenges. Cultural compatibility, technical expertise, and project requirements also influence the optimal location for your team. Carefully consider these factors when making decisions about where to build your distributed team.
Onshore, Nearshore, and Offshore: The Geography of Talent
The geographic location of your team members significantly impacts team dynamics, communication, and project outcomes. Let’s explore the key differences between onshore, nearshore, and offshore teams:
Onshore Teams
Team members are located within the same country as the company’s headquarters.
- Advantages: Shared time zones, cultural alignment, and ease of communication.
- Challenges: Limited access to specialized talent pools, higher labor costs.
Nearshore Teams
Team members are located in a neighboring country, often sharing similar time zones and cultural affinities.
- Advantages: Reduced time zone differences, cultural proximity, cost-effective talent.
- Challenges: Potential language barriers and differences in business practices.
Offshore Teams
Team members are located in a distant country, often with significant time zone differences and cultural variations.
- Advantages: Access to a vast talent pool, lower labor costs.
- Challenges: Overcoming communication barriers, managing time zone differences, and building trust.
While geographical distance is a factor, time zone alignment often has a more significant impact on team dynamics. Nearshore teams often outperform offshore teams due to reduced time zone differences, enabling more synchronous collaboration. More on that here.
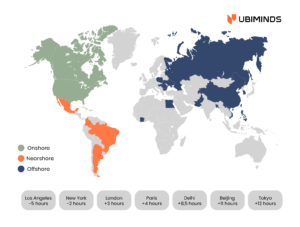
When comparing Onshore, Nearshore and Offshore Services, Brazil’s Location and TimeZone overlap are a bonus to US companies
Why Distributed Teams? Pros and Cons
While distributed teams offer numerous advantages, they can also present unique challenges if managed remotely wrong.
Pros:
- Access to global talent
- Cost-efficiency
- Increased flexibility
- 24/7 operations
Cons:
- Communication challenges
- Time zone differences
- Cultural disparities
- Lack of face-to-face interaction
When to Consider a Distributed Team
Distributed teams can be beneficial at various stages of a company’s lifecycle.
- Startup Phase: To access specialized skills or reduce costs.
- Growth Stage: To scale operations and enter new markets.
- Mature Stage: To optimize resource allocation and enhance innovation.
Building a Distributed Team: Key Considerations
Assembling a high-performing distributed team requires careful planning.
- Talent Acquisition: Sourcing top talent from diverse geographical locations.
- Team Composition: Balancing skill sets and cultural fit.
- Technology Infrastructure: Implementing robust tools for communication and collaboration.
- Legal and HR Considerations: Navigating employment laws and benefits across borders.
The Cost Factor: Distributed vs. Colocated Teams
While distributed teams can offer cost advantages, it’s essential to consider all expenses.
- Infrastructure costs: Cloud-based tools, communication platforms, and security measures.
- Talent acquisition costs: Recruitment, onboarding, and training expenses.
- Employee benefits: Providing competitive benefits packages to remote workers.
- Travel expenses: Occasional in-person meetings and team-building events.
The Five Building Blocks of High-Performing Distributed Teams
Struggling to harness the full potential of a distributed team? You’re not alone. Here’s how to turn that challenge into your biggest asset. This article explores essential best practices for creating and managing high-performing distributed teams.
From understanding different team models to mastering communication and culture across geographies, we’ll cover everything you need to maximize your distributed workforce’s potential.
To achieve peak performance, focus on these essential remote work management pillars:
- Strategic Human Capital Management (HCM): Data-driven approach to talent optimization.
- Talent Acquisition: Building a world-class team through effective recruitment.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Fostering a culture of belonging and innovation.
- Team Autonomy and Empowerment: Delegating authority for maximum impact.
- Ownership and Championing: Cultivating a culture of accountability and initiative.
Ready to dive in? Then let’s explore these fundamental elements in detail!

The Role of Leadership in Leading Remote Teams involves understanding the nuances of Distributed Team Management and creating strategies that ensure effective collaboration and trust. Photo by Lala Azizli.
1. Strategic Human Capital Management (HCM)
A data-driven approach to managing human capital is essential for building successful distributed teams. Focusing on employee well-being and engagement through initiatives like wellness programs and career development opportunities can optimize your talent pool and drive performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Utilize HR analytics to identify trends, optimize processes, and make informed decisions.
- Talent Segmentation: Categorize employees based on skills, potential, and performance to tailor development plans.
- Performance Management: Implement a performance management system aligned with organizational goals.
- Employee Experience: Prioritize employee well-being and engagement through initiatives like wellness programs and career development opportunities.
By establishing People Analytics, for example, you can set KPIs for your HR – or OKRs for the company as a whole – and unravel metrics such as:
- Turnover rate;
- The time you take to finish each phase of the hiring process;
- How satisfied are your employees with the company;
- How your employees do see the company and talk about it to family and friends;
- Simulate multiple scenarios, fixing what’s not working and getting worthy insights, and so on.
2. Talent Acquisition: Building a World-Class Team
It may seem obvious, but I’m going to reinforce it: to have a high-performing team, you need to have the best people with you. Every and each one of them has to be a top performer. And to get there, it’s essential to open your mind to Global Talent Acquisition.
- Employer Branding: Develop a strong employer brand to attract top talent.
- Sourcing Strategies: Utilize various channels to identify potential candidates.
- Candidate Experience: Create a positive candidate experience to increase acceptance rates.
- Skills Assessment: Evaluate candidates based on technical and soft skills.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Prioritize hiring diverse candidates to foster innovation.
A bit of good advice is to create an Employee Value Proposition (EVP) referring to the benefits and rewards employees receive in return for their performance at your company, for example. You can:
- Take good care of your Social Media channels, and add behind-the-scenes action that shows how much you value your team members, moments of teamwork, celebrations, and so on.
- Secure a spot in your website to detailed talk about the open positions, career opportunities and options, and maybe even include some testimonials from a few of your current team members.
- Find a partner like Ubiminds that helps you to promote your open positions abroad.
It’s important to have in mind that senior tech talents, nowadays, pick the company they want to work in, not the other way around. They are less concerned about the paycheck at the end of the month, and go for healthier, more flexible workspaces, with trusted leadership and Diversity and Inclusion — which leads us to the next topic.
3. Diversity and Inclusion: Fostering Innovation and Collaboration
Virtual team collaboration is amplified in a distributed environment, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing across borders. Thus, Diversity and inclusion (D&I) are essential components of high-performing distributed teams.
By embracing differences, organizations can unlock innovation, improve decision-making, and enhance employee satisfaction.
Beyond Representation: The Importance of Inclusion
Diversity refers to the presence of differences, while inclusion focuses on creating an environment where everyone feels valued and respected. True D&I goes beyond representation and addresses equity and belonging.
When you work with a high-performing distributed team, — by nearshoring, for example — it’s undeniable that the act of sharing knowledge and experience gets really amplified. You get to have your local and remote team combining senior software experts from the most different backgrounds. Counting in professional, cultural, and social life.
Having a diverse, prejudice-free work environment extremely helps to promote good, innovative ideas. Also, a diverse team means a bigger repertoire of references and benchmarks. This impacts directly on your co-worker’s ability to problem-solve and boost the chances of your team reflecting your users’ base, among other perks. Keep that in mind.
Building an Inclusive Culture
To enhance DEIB, your HR can think of hackathons, trading experience events, working in temporary squads, or even setting up book clubs or contests. The idea is to get the best out of your high-performing distributed team and mingle them up.
Also consider:
- Unconscious Bias Training: Educate employees about unconscious biases and their impact (more on this in our antibias article).
- Employee Resource Groups (ERGs): Create safe spaces for underrepresented groups to connect and support each other.
- Mentorship and Sponsorship Programs: Provide opportunities for career development and advancement.
- Accessibility: Ensure the workplace is accessible to employees with disabilities.
- Inclusive Leadership: Foster a culture of inclusivity from the top down.

Diversity Fuels Innovation! Struggling to build a diverse and inclusive software development team? Learning about affinity bias, intercultural competence, and micro affirmations may be the way to improve Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging (DEIB) in your team! Photo by Surface.
4. Team Autonomy and Empowerment
Empowering teams is essential for driving innovation and productivity in a distributed environment. By granting autonomy and fostering a culture of ownership, organizations can unlock the full potential of their workforce.
The Importance of Autonomy
People at the top of their game want to be recognized as the senior professionals they are. Granting them autonomy leads to:
- Increased motivation: Employees are more engaged when they have control over their work.
- Improved problem-solving: Empowered teams can make quicker and more informed decisions.
- Enhanced creativity: Autonomy fosters innovation and experimentation.
- Stronger sense of ownership: Employees are more invested in the success of the project.
Balancing Autonomy with Accountability
If you give the team freedom, how do you ensure they deliver? We’ll dive deeper later, but best practices include:
- Clear expectations: Define roles, responsibilities, and performance metrics.
- Regular check-ins: Maintain open distributed team communication and provide guidance.
- Celebrate successes: Recognize and reward team achievements.
Building a Culture of Empowerment
Top engineers will only join companies that have relevant missions, and offer interesting challenges and room for growth. That is why we highlight the importance of preparing a mindset and culture, especially among leaders.
High-performing distributed teams urge for a specific type of leader, one that is willing to trust the team’s self-accountability and proactivity, instead of constantly charging in and breaking your employee’s flux of ideas. Discuss:
- Trust and delegation: Empower team members to make decisions.
- Decentralized decision-making: Distribute authority throughout the organization.
- Continuous learning and development: Invest in employee growth and skill enhancement.
- Open communication: Foster a culture of transparency and feedback.
It’s much more about empowerment than managing tasks. Leaders that are still controlling effort and micromanaging to-dos will definitely fall behind. The focus needs to be on delivered outcomes and deadlines instead of output. Good steps are to implement.
5. Championing Continuous Improvement
A strong sense of ownership and accountability is crucial for the success of distributed teams. By empowering team members to take initiative and champion their work, organizations can build a high-performance culture.
Fostering a culture of ownership and accountability is essential for high-performing distributed teams. By empowering team members to take initiative and champion their work, organizations can drive innovation and improve overall performance.
Cultivating a Sense of Ownership
- Define clear roles and responsibilities: Ensure each team member understands their role and contributions.
- Empower decision-making: Grant autonomy to team members to make decisions within their scope.
- Celebrate successes: Recognize and reward individual and team achievements.
Championing Continuous Improvement
- Encourage a growth mindset: Foster a culture of learning and development.
- Implement feedback mechanisms: Create opportunities for regular feedback and reflection.
- Experimentation and innovation: Support a culture of trying new ideas and approaches.
- Knowledge sharing: Encourage collaboration and knowledge transfer within the team.
High-performing distributed teams are the future of work. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can build a cohesive, productive, and engaged team that thrives, no matter where your team members are located. Embrace the challenges and leverage the opportunities of distributed work to lead your team to success.
Struggling to find the perfect talent pool for your tech company? Building successful remote teams allows you to tap into a global network of skilled professionals. Ubiminds offers actionable strategies to enhance your distributed workforce and ensure success across borders. Reach out to build or scale a distributed team in Latin America:
FAQ for High-Performing Distributed Teams
Q: What are the benefits of building a distributed team?
A: Access to global talent, increased flexibility, cost savings, and 24/7 coverage.
Q: What tools do I need to build a successful distributed team?
A: Collaboration platforms like Slack and Zoom, project management tools like Asana, and knowledge sharing platforms like Confluence.
Q: How do you overcome time zone challenges in distributed teams?
A: Implement core hours, use asynchronous communication tools, and schedule meetings strategically.

International Marketing Leader, specialized in tech. Proud to have built marketing and business generation structures for some of the fastest-growing SaaS companies on both sides of the Atlantic (UK, DACH, Iberia, LatAm, and NorthAm). Big fan of motherhood, world music, marketing, and backpacking. A little bit nerdy too!








